The term
Viking commonly denotes the ship-borne
warriors,
pirates and traders of
Norsemen (literally, men from the north) who originated in
Scandinavia and raided the coasts of
Britain,
Ireland and mainland Europe as far east as the
Volga River in
Russia (referred to as
Varangians by the Russian
Primary Chronicle) The pre-Christian Scandinavian population is also referred to as
Norse, although that term is properly applied to the whole civilization of Old-Norse speaking people.
Mountains Peninsula Viking Age Varangian Viking Thing (assembly) Christianization Kalmar Union Denmark–Norway Sweden–Finland Sweden–Norway Scandinavia Denmark Finland Norway Sweden Iceland Scandinavism Monetary Union Defence union Royal League SAS Etymology See main article Viking Age.
The period from the earliest recorded raids in the 790s until the
Norman Conquest of England in 1066 is commonly called the "Viking Age." The
Normans, however, were descended from
Norwegians (in Norwegian they are still to date refered to as
jeg er en Normann),
Orkney,
Hiberno-Norse, and
Danelaw Vikings who were given
feudal overlordship of areas of northern France — the
Duchy of Normandy — in the
8th century. In that respect, the Vikings continued to have an influence in northern Europe. Likewise, King
Harold Godwinson, the last
Anglo-Saxon king of England who was killed during the Norman invasion in 1066, was descended from Danish Vikings. Many of the medieval kings of Norway and Denmark were married to English and Scottish royalty and Viking forces were often a factor in dynastic disputes pre-1066.
Geographically, a "Viking Age" may be assigned not only to the Scandinavian lands (modern Denmark, Norway and Sweden), but also to territories under
North Germanic dominance, mainly the
Danelaw, which replaced the powerful
English kingdom of
Northumbria and the
Isle of Man. Contemporary with the European Viking Age, the
Byzantine Empire in the
Balkans and
Anatolia, heir to the
Eastern Roman Empire, experienced the greatest period of stability (circa 800–1071) it would enjoy after the initial wave of
Arab conquerors in the
7th century.
Viking navigators also opened the road to new lands to the north, to the west and to the east resulting in the foundation of independent kingdoms in the
Shetland,
Orkney, and
Faroe Islands,
Iceland,
Greenland, and
L'Anse aux Meadows, a short-lived settlement in
Newfoundland, circa 1000 A.D. Many of these lands, specifically Greenland and Iceland, were likely discovered by sailors blown off course. Greenland was later abandoned because its few "green" spots disappeared due to climate change. Vikings also seized and destroyed many villages and territories in
Slavic-dominated areas of
Eastern Europe.
During three centuries, Vikings appeared along the coasts and rivers of Europe, as traders generally, but also as raiders when opportunity allowed, and even like
Turgesius, as settlers. From 839,
Varangian mercenaries in
Byzantine service, notably
Harald Hardrada, campaigned in
North Africa,
Jerusalem, and other places in the
Middle East. Important trading ports during the period include
Birka,
Hedeby,
Kaupang,
Jorvik,
Staraya Ladoga,
Novgorod and
Kiev. Generally speaking, the
Norwegians expanded to the north and west to places such as
Iceland and
Greenland, the
Danes to England and France, settling in the
Danelaw (NE England) and
Normandy, and the
Swedes to the east. These nations, although distinct, were similar in culture, especially
language. The names of Scandinavian kings are known only for the later part of the Viking Age, and only after the end of the Viking Age did the separate kingdoms acquire a distinct identity as nations, which went hand in hand with their
Roman Catholicization. Thus the end of the Viking Age (9th–11th century) for the Scandinavians also marks the start of their relatively brief Middle Ages.
There is archaeological evidence (coins) that the Vikings reached the city of
Baghdad, the centre of the Islamic Empire and their considerable intellectual endeavours. In 921,
Ibn Fadlan was sent as emissary on behalf of the
Caliph of
Baghdad to the iltäbär (vassal-king under the Khazars) of the Volga Bulgaria, Almış. The Bolgar King had petitioned to the Caliph to establish relations. He had asked to have someone come to teach him Arabic and the Qu'ran and pledge allegiance to Hanafi rite of the Sunni Muslims. The Caliph promised to send money to build a fort on the Volga, but the transaction never occurred. The Norse regularly plied the Volga with their trade goods: furs, tusks, seal fat to seal boats and slaves (notably female slaves; this was the one time in the history of the slave-trade when females were priced higher than males). However, they were far less successful in establishing settlements in the Middle East, due to the more centralized
Islamic power, namely of the
Umayyad and, later,
Abbasid empires.
The Viking Age After trade and settlement, cultural impulses flowed from the rest of Europe. Christianity had had an early and growing presence in Scandinavia, and with the rise of centralized authority along with a stiffening of coastal defense in the areas the Vikings preyed upon, the Viking raids became more risky and less profitable. With the rise of kings and great nobles and a quasi-
feudal system in Scandinavia, they ceased entirely – in the 11th century the Scandinavians are frequently chronicled as combating the Vikings from the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea , which would eventually lead to Danish and Swedish participation in the
Baltic crusades (end of 12th and early 13th century) and contributed to the development of the
Hanseatic League.
The east Baltic world was transformed by military conquest: First the Livs, Letts and Estonians, then the Prussians and the Finns underwent defeat, baptism, military occupation and sometimes extermination by groups of Germans, Danes and Swedes.
Decline Traditionally the earliest date given for a Viking raid is 787 when, according to the
Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, a group of men from
Norway sailed to
Portland, in Dorset. There, they were mistaken for merchants by a royal official, and they murdered him when he tried to get them to accompany him to the king's manor to pay a trading tax on their goods. The next recorded attack, dated
June 8,
793, was on the monastery at
Lindisfarne on the east coast of
England. For the next 200 years,
European history is filled with tales of Vikings and their plundering; the majority of chronicles comes from western witnesses or their descendants, a lesser quantity of chronicles comes from eastern mentions from the
Nestor chronicles,
Novgorod chronicles,
Ibn Fadlan chronicles,
Ibn Ruslan chronicles, and many brief mentions of the Fosio bishop from the first big attack to the
Byzantine empire.
The vikings had little influence throughout the coastal areas of
Ireland and
Scotland but they conquered and colonised large parts of England (see
Danelaw), and conquered large coastal territories in the
Baltic Sea and a large part of inland Russian territories across the rivers settled in
Staraya Ladoga,
Novgorod and along major waterways to the
Byzantine empire.
Wales also saw some Viking settlements on its coast; the modern day city of
Swansea takes its name from Sweyne Forkbeard who was shipwrecked at modern day
Swansea Bay; neighbouring
Gower Peninsula has many place names of Norse origin (such as
Worms Head; worm is the Norse word for dragon, as the Vikings believed that the serpent-shaped island was a sleeping dragon). Twenty miles west of
Cardiff on the
Vale of Glamorgan coast is the semi-flooded island of
Tusker Rock, which takes its name from Tuska, the Viking whose people semi-colonised the fertile lands of the
Vale of Glamorgan.
The Britons of
Cornwall allied with Danish Vikings in 722 to defeat the Saxons of
Wessex at "Hehil", possibly somewhere near modern day Padstow; this battle is recorded in the Analies Cambria and kept Cornwall free of Anglo-Saxon control for at least 100 years. The Danes tactically helped their Cornish allies by making devastating pillaging raids on Wessex which weakened the authority of the Saxons, and in 1013 Wessex was conquered by the Danes under the leadership of the Viking King of Denmark
Sweyn Forkbeard.
Vikings travelled up the rivers of
France and
Spain, and gained control of areas in
Russia and along the
Baltic coast. Stories tell of raids in the
Mediterranean and as far east as the
Caspian Sea.
In select cases, the
Celtic nations of Scotland, Ireland, Wales,
Brittany in 865 and in 722
Cornwall, during their battles against the
Anglo-Saxons, decided to ally with the Vikings against the Saxons.
Adam of Bremen records in his book
Gesta Hammaburgensis Ecclesiae Pontificum, (volume four):
"There is much gold here (in
Zealand), accumulated by piracy. These pirates, which are called
wichingi by their own people, and
Ascomanni by our own people, pay tribute to the Danish king."
Egil Skallagrimsson writes;
Björn var farmaður mikill, var stundum í víking, en stundum í kaupferðum, in English: "Björn was a great traveller; sometimes as Viking, sometimes as tradesman".
Aurum ibi plurimum, quod raptu congeritur piratico. Ipsi enim piratae, 'quos illi Wichingos as appellant, nostri Ascomannos regi Danico tributum solvunt.
 Historical records Norse mythology
Historical records Norse mythology,
Norse sagas and
Old Norse literature tell us about their religion through tales of heroic and mythological heroes. However, the transmission of this information was primarily oral, and we are reliant upon the writings of (later) Christian scholars, such as the Icelanders
Snorri Sturluson and
Sæmundur fróði, for much of this. Many of these sagas were written in
Iceland, and most of them, even if they had no Icelandic provenance, were preserved there after the Middle Ages due to the Icelanders' continued interest in Norse literature and law codes.
Vikings in those sagas are described as if they often struck at accessible and poorly defended targets, usually with impunity. The sagas state that the Vikings built settlements and were skilled craftsmen and traders.
The writer Snorri Sturlason wrote about the Norwegian kings, and is famous for his Sagas(Kongesagaene/King's Saga) about the Norwegian kings until his present day. Like Snorri Sturlason, Icelanders at that time were Norwegian in both language and culture,because of the Norwegian rule, but evolved more and more into their own liking because of the isolation from the mainland.
Icelandic sagas Viking expansion Britain According to the
Anglo-Saxon Chronicles, after
Lindisfarne was raided in 793, Vikings continued on small-scale raids across England. Viking raiders struck England in 793 and raided a Christian monastery that held Saint Cuthbert's relics. The raiders killed the monks and captured the valuables. This raid was called the beginning of the "Viking Age of Invasion", made possible by the Viking longship. There was great violence during the last decade of the 8th century on England's northern and western shores. While the initial raiding groups were small, it is believed that a great amount of planning was involved.
During the winter between 840 and 841, the Norwegians raided during the winter instead of the usual summer. They waited on an island off Ireland. In 865 a
large army of Danish Vikings, supposedly led by Ivar, Halfdan and Guthrum arrived in East Anglia. They proceeded to cross England into Northumbria and captured York (
Jorvik), where some settled as farmers. Most of the English kingdoms, being in turmoil, could not stand against the Vikings, but
Alfred of Wessex managed to keep the Vikings out of his country. Alfred and his successors continued to drive back the Viking frontier and take York.
A new wave of Vikings appeared in England in 947 when
Erik Bloodaxe captured York. The Viking presence continued through the reign of
Canute the Great (1016-1035), after which a series of inheritance arguments weakened the family reign. The Viking presence dwindled until 1066, when the Norwegians lost their final battle with the English. See also
Danelaw.
The Vikings did not get everything their way. In one instance in England, a small Viking fleet attacked a rich monastery at
Jarrow. The Vikings were met with stronger resistance than they expected: their leaders were killed, the raiders escaped, only to have their ships beached at Tynemouth and the crews killed by locals. This was one of the last raids on England for about 40 years. The Vikings instead focused on Ireland and Scotland. There was a good deal of intermarriage between the Vikings and the Anglo-Saxons.
England While there are few records from the earliest period, it is believed to be clear that a Scandinavian presence in Scotland increased in the 830s. In 836, a large Viking force believed to be Norwegian invaded the Earn valley and
Tay valley which were central to the
Pictish kingdom. They slaughtered Eoganan, king of the Picts, and his brother, the vassal king of the Scots. They also killed many members of the Pictish aristocracy. The sophisticated kingdom that had been built fell apart, as did the Pictish leadership. The foundation of
Scotland under
Kenneth MacAlpin is traditionally attributed to the aftermath of this event.
The isles to the north and west of Scotland were heavily colonized by Norwegian Vikings.
Shetland,
Orkney, the
Western Isles,
Caithness and
Sutherland were under Norse control, sometimes as fiefs under the King of Norway and other times as separate entities. Shetland and Orkney were the last of these to be incorporated into Scotland in as late as 1468. The Vikings almost never settled on the Scottish main land but some did settle on Orkney and Shetland..
Scotland Wales was not colonized by the Vikings as heavily as eastern England and Ireland. The Vikings did, however, settle in the south around
St. David's,
Haverfordwest, and
Gower, among other places. Place names such as Skokholm, Skomer, and Swansea remain as evidence of the Norse settlement., and ultimately, the Saxons were unable to conquer Wales, partly as in 1013 the Saxons were themselves conquered by the Vikings and annexed to a Danish empire controlled by
King Canute.
Wales In 722 the
Cornish allied with
Danish Vikings in order to hold
Wessex from expanding into
Cornwall. A Wessex
Saxon army led by
King Ine was comprehensively destroyed by an alliance of Cornish and Vikings near the Camel estuary. This battle, as well as the Vikings continually attacking Wessex, enabled Cornwall to stay autonomous from Wessex, and Wessex itself would eventually be conquered by the Danish Vikings in 1013 by the Viking King of Denmark
Sweyn Forkbeard.
Cornwall The Vikings conducted extensive raids in
Ireland and founded many towns, including,
Athlone,
Dublin,
Limerick,
Mullingar,
Wexford, and
Waterford. At some points, they seemingly came close to taking over the whole isle; however, the Scandinavians settled down and intermixed with the Irish. Literature, crafts, and decorative styles in Ireland and the British Isles reflected Scandinavian culture. Vikings traded at Irish markets in Dublin. Excavations found imported fabrics from England, Byzantium, Persia, and central Asia. Dublin became so crowded by the 11th century that houses were constructed outside the town walls.
The Vikings pillaged monasteries on Ireland's west coast in 795, and then spread out to cover the rest of the coastline. The north and east of the island were most affected. During the first 40 years, the raids were conducted by small, mobile Viking groups. From 830 on, the groups consisted of large fleets of Viking ships. From 840, the Vikings began establishing permanent bases at the coasts. Dublin was the most significant settlement in the long term. The Irish became accustomed to the Viking presence & culture. In some cases they became allies and also intermarried throughout all of Ireland.
In 832, a Viking fleet of about 120 ships under
Turgesius invaded kingdoms on Ireland's northern and eastern coasts. Some believe that the increased number of invaders coincided with Scandinavian leaders' desires to control the profitable raids on the western shores of Ireland. During the mid-830s, raids began to push deeper into Ireland. Navigable waterways made this deeper penetration possible. After 840, the Vikings had several bases in strategic locations throughout Ireland.
In 838, a small Viking fleet entered the
River Liffey in eastern Ireland. The Vikings set up a base, which the Irish called
longphorts. This longphort would eventually become Dublin. After this interaction, the Irish experienced Viking forces for about 40 years. The Vikings also established longphorts in Cork, Limerick, Waterford, and Wexford. The Vikings were driven out of Ireland for a short period around 900, but returned to Waterford in 914 to found what would become Ireland's first city. The other longphorts were soon re-occupied and developed into cities and towns.
The last major battle involving Vikings was the
Battle of Clontarf in 1014, in which a large force from the pan-Viking world and their Irish allies opposed
Brian Boru, then the High King of Ireland and his forces, a small contingent of which were Viking defectors. The battle was fought in what is the now Dublin suburb of
Clontarf on Good Friday of that year. Boru, the Irish High King had gracefully allowed the Viking King of Dublin; Sigtrygg Silkbeard, one year to prepare for his coming assault. Silkbeard responded by offering the bed of his mother to several Viking lords from Scandinavia and the British Isles. The savage melee between the heavily mailed Norse and the unarmored, yet undaunted Gaels ended in a rout of the Vikings and their Irish allies. Careful accounts were taken by both sides during the battle, and thus many famous warriors sought each other out for personal combat and glory. High King Brian, who was near verging upon eighty, did not personally engage in the battle but retired to his tent where he spent the day in quiet prayer. History records that the Viking Earl Brodir of Man chanced upon Brian's tent as he fled the field. He and a few followers seized the opportunity, and surprised the High King, killing the aged Brian before being captured. Brian's foster son
Wolf the Quarrelsome later tracked down and dispatched Brodir by disembowelment; Wolf watching as Brodir marched and wound his own innards around the trunk of a large tree. The battle was fairly matched for most of the day and each side had great respect for the prowess of the other, however in the end the Irish forced the Norse to return to the sea. Many of the fleeing Vikings were drowned in the surf by their heavy mail coats as they struggled for the safety of their longships; others were pursued and slain further inland. After the battle, Viking power was broken in Ireland forever, though many settled Norse remained in the cities and prospered greatly with the Irish through trade. With Brian dead, Ireland returned to the fractured kingdom it had once been, but was now cleared of further Viking predation.
Ireland West Francia suffered more severely than
East Francia during the Viking raids of the ninth century, which destroyed the
Carolingian Empire, though it suffered less severely than the
Low Countries. The reign of
Charles the Bald, whose military record was one of consistent failure, coincided with some of the worst of these raids, though he did take action by the
Edict of Pistres of 864 to secure a standing army of cavalry under royal control to be called upon at all times when necessary to fend off the invaders. He also ordered the building of fortified bridges to prevent inland raids.
Nonetheless, the
Bretons allied with the Vikings and
Robert, the
margrave of
Neustria, (a march created for defence against the Vikings sailing up the
Loire), and
Ranulf of Aquitaine died in the
Battle of Brissarthe in 865. The Vikings also took advantage of the civil wars which ravaged the
Duchy of Aquitaine in the early years of Charles' reign. In the 840s,
Pepin II called in the Vikings to aid him against Charles and they settled at the mouth of the
Garonne. Two
dukes of Gascony,
Seguin II and
William I, died defending
Bordeaux from Viking assaults. A later duke,
Sancho Mitarra, even settled some at the mouth of the
Ardour in an act presaging that of
Charles the Simple and the
Treaty of Saint-Clair-sur-Epte by which the Vikings were settled in
Rouen, creating
Normandy as a bulwark against other Vikings.
West Francia By the mid 9th century, though apparently not before (Fletcher 1984, ch. 1, note 51), there were Viking attacks on the coastal
Kingdom of Asturias in the far northwest of the peninsula, though historical sources are too meagre to assess how frequent or how early raiding occurred. By the reign of
Alfonso III Vikings were stifling the already weak threads of sea communications that tied
Galicia (a province of the Kingdom) to the rest of Europe. Richard Fletcher attests raids on the Galician coast in 844 and 858: "Alfonso III was sufficiently worried by the threat of Viking attack to establish fortified strong points near his coastline, as other rulers were doing elsewhere." In 861, a group of Vikings ransomed the king of Pamplona, whom they had captured the previous year, for 60,000 gold pieces.
Raiding continued for the next two centuries. In 968 Bishop Sisnando of
Compostela was killed, the monastery of Curtis was sacked, and measures were ordered for the defence of the inland town of
Lugo. After
Tui was sacked early in the 11th century, its bishopric remained vacant for the next half-century. Ransom was a motive for abductions: Fletcher instances Amarelo Mestáliz, who was forced to raise money on the security of his land in order to ransom his daughters who had been captured by the Vikings in 1015. Bishop
Cresconio of Compostela (ca. 1036–66) repulsed a Viking foray and built the fortress at
Torres del Oeste (Council of
Catoira) to protect Compostela from the Atlantic approaches. The city of
Póvoa de Varzim in Northern
Portugal, then a town, was settled by Vikings around the 9th century and its influence kept strong until very recently, mostly due to the practice of
endogamy in the community.
In the Islamic south, the first navy of the
Emirate was built after the humiliating Viking ascent of the
Guadalquivir in 844. Nevertheless, in 859, Danish pirates sailed through Gibraltar and raided the little Moroccan state of Nakur. The king's harem had to be ransomed back by the emir of Cordoba. These and other raids prompted a ship-building program at the dockyards of
Seville. The Andalusian navy was thenceforth employed to patrol the Iberian coastline under the caliphs
Abd al-Rahman III (912–61) and
Al-Hakam II (961–76). By the next century, piracy from North Africans superseded Viking raids.
Iberia Some exploration and expansion occurred still further west, in modern-day Greenland and Newfoundland, with exploration led by
Eric the Red and his son,
Leif Erikson from Iceland. Permanent settlements were established, L'anse Aux Meadows being excavated in modern times. The Icelanders were insufficient in numbers and technological superiority to overwhelm or overawe the local Native Americans (called
Skraelings) which means in old-Norse, weaklings. Colonization efforts were strictly limited to opportunistic families who could not obtain good land elsewhere, the best lands of Iceland having been taken years earlier and Greenland proving a harsh environment. The Icelandic Vikings never did try to invade "Vinland," or as we know it today as Newfoundland. Although there were some skirmishes, such activity was an attempt to colonize.
In 1931 a railroad brakeman named James Edward Dodd found a broken sword and fragments of an axe and shield near Beardmore Ontario east of Lake Nippigon. Upon extensive examination European Norse experts agreed that the relics were authentic Norse weapons.
[1] Similarly an artifact called the
Kensington Runestone was unearthed in 1898 by a Norwegian-American farmer in West-Central Minnesota. Now residing in a Minnesota Museum, the stone carries and inscription that depicts an attack on a party of Goths and Norwegians that took place in 1362. The authenticity of this artifact is in dispute.
[2]  North America
North America Two areas along Greenland's southwest coast were colonized by Norse settlers ca. 986 AD. The land was marginal at best. The settlers arrived during a warm phase, when short-season crops such as rye and barley could be grown. Sheep and hardy cattle were also raised for food, wool, and hides. Their main export was
walrus ivory, which was traded for iron and other goods which could not be produced locally. Greenland became a dependency of the king of Norway in 1261. During the 13th century, the population may have reached as high as 5,000, divided between the two main settlements of
Austrbygd and
Vestrbygd. Greenland had several churches and a cathedral at
Gardar. The
Catholic diocese of Greenland was subject to the archdiocese of
Nidaros. However, many bishops chose to exercise this office from afar. As the years wore on, the climate shifted (qv.
little ice age) and elephant ivory from Africa became increasingly available. Crops failed and trade declined. The Greenland colony gradually faded away. By 1450 it had lost contact with Norway and simply disappeared from all but a few Scandinavian legends.
Greenland The Vikings prolific expansion is still exhibited in modern genetics. Relatively high frequencies of Haplogroup
R1a1 are found in
Northern Europe, the largest being 23% in Iceland, and it is believed to have been spread across
Europe by the
Indo-Europeans and later migrations of
Vikings, which accounts for the existence of it in, among other places, the
British Isles.
[3] Genetics Why the Viking expansion took place is a much debated topic in Nordic history, and there are no clear answers.
One common theory is that the Viking homelands were
overpopulated. A growing population or a lack of ability of
agriculture to support the existing population could have caused a lack of land. For people living near the coast in possession of good naval technologies, it makes sense to expand overseas in the course of a typical
youth bulge effect. One problem with this explanation is that, as a result of the lack of sources, no such rise in population or decline in agricultural production has been proven. This theory is widely accepted as part of the solution, since it is hard to imagine why a people would colonise new territories if there was not a lack of land at home. However, it does little to explain the plundering raids and trading expeditions, or why the expansion went to overseas countries and not into the big, uncultivated forest areas of the Viking homelands on the
Scandinavian peninsula.
Another explanation is that the Vikings used temporary weakness in the regions they travelled to. For instance, the Danish Vikings were aware of the internal division of the
empire of
Charlemagne that began in the 830s and resulted in the splitting up of the empire. The Danish expeditions in
England also profited from the disunity of the different English kingdoms.
The decline of old
trade routes could also be a part of the explanation. The
trade between western Europe and the rest of the
Eurasian continent had suffered from a severe decline as a result of the fall of the
Roman Empire in the 5th century and the expansion of
Islam in the 7th century. At the time of the Viking, the trade on the
Mediterranean Sea was at its lowest level. By, for instance, trading
furs and
slaves against
silver and
spices with the Arabs, and then trading the silver and spices for
weapons with the
Franks, the Vikings profited from international trade, picking up the role the declining Mediterranean trade had previously filled.
Another important factor when it comes to trade is that the destruction of the
Frisian fleet by the Franks. This gave the Vikings the opportunity to take over its old markets. However, both the explanation underlining disunity and the one underlining trade explains how the expansion was possible, more than why it occurred. This is why we can consider that in addition to the economic factor, there is also another reason of first Vikings' raids, they could also originate in resistance to forced Christianisation, in particular Charlemagne's persecutions against all the Pagan people: who have to accept "conversion or the massacre".
Snorri Sturluson in the
saga of St Olafr chapter 73, describes the brutal process of Christianisation in
Norway :
" those who did not give up paganism were banished, with others he (St Olafr) cut off their hands or their feet or extirpated their eyes, others he ordered hanged or decapitated, but did not leave unpunished any of those who did not want to serve God (...) he afflicted them with great punishments (...) He gave them clerks and instituted some in the districts". Clerical pressure by violence since
Charlemagne can explain partly the Vikings'
strandhögg targeting of Christian buildings.
Explanations of the expansion Archaeology Main article: Rune stone Rune stones There are numerous burial sites associated with Vikings. Some examples include:
Gettlinge gravfält,
Öland, Sweden, ship outline
Jelling, Denmark, a World Heritage Site
Oseberg, Norway.
Gokstad, Norway.
Tuna, Sweden.
Hulterstad gravfält, near the villages of
Alby and Hulterstad,
Öland, Sweden, ship outline of standing stones
Burial sites There were two distinct classes of Viking ships: the
longship (sometimes erroneously called "drakkar", a corruption of "dragon" in Norse) and the
knarr. The longship, intended for warfare and exploration, was designed for speed and agility, and were equipped with oars to complement the sail as well as making it able to navigate independently of the wind. The longship had a long and narrow hull, as well as a shallow draft, in order to facilitate landings and troop deployments in shallow water. The knarr, on the other hand, was a slower merchant vessel with a greater cargo capacity than the longship. It was designed with a short and broad hull, and a deep draft. It also lacked the oars of the longship.
Longships were used extensively by the
Leidang, the Scandinavian defense fleets. The term "Viking ships" has entered common usage, however, possibly because of its romantic associations (discussed below).
In Roskilde are the well-preserved remains of five ships, excavated from nearby
Roskilde Fjord in the late 1960s. The ships were scuttled there in the 11th century to block a navigation channel, thus protecting the city, which was then the Danish capital, from seaborne assault. These five ships represent the two distinct classes of the Viking Ships, the longship and the knarr.
Longships are not to be confused with
longboats.
Ships Early modern publications, dealing with what we now call Viking culture, appeared in the 16th century, e.g.
Historia de gentibus septentrionalibus (Olaus Magnus, 1555), and the first edition of the 13th century
Gesta Danorum of
Saxo Grammaticus in 1514. The pace of publication increased during the 17th century with Latin translations of the
Edda (notably Peder Resen's
Edda Islandorum of 1665).
See also 19th century Viking revival. Modern revivals The word
Viking was popularized, with positive connotations, by
Erik Gustaf Geijer in the poem,
The Viking, written at the beginning of the 19th century. The word was taken to refer to romanticized, idealized naval warriors, who had very little to do with the historical Viking culture. This renewed interest of
Romanticism in the Old North had political implications. A myth about a glorious and brave past was needed to give the Swedes the courage to retake
Finland, which had been lost in 1809 during the
war between Sweden and Russia. The
Geatish Society, of which Geijer was a member, popularized this myth to a great extent. Another Swedish author who had great influence on the perception of the Vikings was
Esaias Tegnér, member of the
Geatish Society, who wrote a modern version of
Friðþjófs saga ins frœkna, which became widely popular in the Nordic countries, the
United Kingdom and
Germany.
A focus for early British enthusiasts was George Hicke, who published a
Linguarum vett. septentrionalium thesaurus in 1703–05. During the 18th century, British interest and enthusiasm for Iceland and Nordic culture grew dramatically, expressed in English translations as well as original poems, extolling Viking virtues and increased interest in anything Runic that could be found in the Danelaw, rising to a peak during
Victorian times.
Romanticism Main article: Nazi mysticism Living history Main article: Germanic neopaganism Neopaganism Popular culture Popular misconceptions Legend had it that the Vikings were very tall and large men.
Ibn Fadlan and various European sources mention that the Vikings were of great stature. A number of modern studies have been conducted which show Vikings to have been on average between 168.4 cm (66.3in) and 176 cm (69.3in) tall. There is variation, and higher ranking Vikings tended to be taller (likely due to better nutrition), but the Vikings were, compared to people of today, not unusually tall. However, when compared to the people that lived during the Viking era, Vikings were indeed taller (which is highly attributable to genetic factors).
Height Main article: Horned helmet Horned helmets Despite images of Viking marauders who live for
plunder and
warfare, the heart of Viking society was reciprocity, on both a personal, social level and on a broader political level. The Vikings lived in a time when numerous societies were engaged in many violent acts, and the doings of the Vikings put into context are not as savage as they seem. Others of the time period were much more savage than the Vikings, such as the Frankish king,
Charlemagne, who cut off the heads of 4,500 Saxons (
Bloody Verdict of Verden) in one day, partly because they would not accept the Christian faith. Most Vikings were traders, although some did plunder, often monasteries around Ireland, Scotland, Wales and England, as they had a lot of valuables in gold and silver. As monasteries were centers of learning & writing, their experiences were much more likely to enter the historical record. However, considerable literature in the monasteries would have been destroyed during the plunderings.
One of the Vikings' largest profit-centres was the
slave trade; any group that acts as slave-takers is likely to be viewed with disdain by their victims. During the period of the Vikings, slavery was common throughout Northern Europe, and the fact that many slaves were captured persons was irrelevant in law. A person from
Poland could be captured and later sold in
England, for example.
Slavery was common amongst the Scandinavians themselves, as well.
In the 300-year period where Vikings were most active, there were only approximately 347 attacks that spread from the British Isles to Morocco, Portugal, and Turkey. In Ireland, where the Vikings are most famous for attacking monasteries, there were only 430 known attacks during this 300-year period.
Savage marauders Main article: Skull cups Skull cups The image of wild-haired, dirty savages sometimes associated with the Vikings in popular culture is a distorted picture of reality. Non-Scandinavian Christians are responsible for most surviving accounts of the Vikings and, consequently, a strong possibility for bias exists. This attitude is likely attributed to Christian misunderstandings regarding paganism. Viking tendencies were often misreported and the work of
Adam of Bremen, among others, told largely disputable tales of Viking savagery and uncleanliness.
However, it is now known that the Vikings used a variety of tools for personal grooming such as combs, tweezers, razors or specialized "ear spoons". In particular, combs are among the most frequent artifacts from Viking Age excavations. The Vikings also made
soap, which they used to bleach their hair as well as for cleaning, as blonde hair was ideal in the Viking culture.
The Vikings in
England even had a particular reputation for excessive cleanliness, due to their custom of bathing once a week, on Saturdays (unlike the local
Anglo-Saxons). To this day, Saturday is referred to as
laugardagur/
laurdag/
lørdag/
lördag, "washing day" in the
Scandinavian languages, though the original meaning is lost in modern speech in most of the Scandinavian languages ("laug" still means "bath" or "pool" in Icelandic).
As for the
Rus', who had later acquired a subjected
Varangian component,
Ibn Rustah explicitly notes their cleanliness, while
Ibn Fadlan is disgusted by all of the men sharing the same, used vessel to wash their faces and blow their noses in the morning. Ibn Fadlan's disgust is probably motivated by his ideas of personal hygiene particular to the Muslim world, such as running water and clean vessels. While the example intended to convey his disgust about the customs of the Rus', at the same time it recorded that they did wash every morning.
Fiction Olaf Tryggvason. Forced thousands to convert to Christianity. Once burned London Bridge down out of anger of people disobeying his orders (hence the childrens' rhyme "
London Bridge is Falling Down").
Sweyn Forkbeard, king of
Denmark,
England,
Norway and founder of
Swansea ("Sweyn's island")
Magnus Barelegs, King of Norway
Askold and Dir, legendary
Varangian conquerors of
Kiev Helgi or
Oleg, ruler of
Kiev Björn Ironside, son of
Ragnar Lodbrok, pillaged in
Italy Brodir,
Danish Viking who killed the High King of
Ireland,
Brian Boru Egill Skallagrímsson, Icelandic warrior and
skald (see also
Egils saga)
Erik the Red, discoverer of
Greenland Leif Ericsson, discoverer of
Vínland, son of
Erik the Red Freydís Eiríksdóttir, a Viking woman who sailed to
Vínland Canute the Great, the most successful Danish Viking King. Son of
Sweyn Forkbeard, grandson of
Harold Bluetooth and great great uncle to
William the Conqueror. This connection was one of the key justifications for William's claim to the
English throne.
Harald Hardrada, Norwegian king who unsuccessfully tried to conquer
England in 1066
Gardar Svavarsson, discoverer of Iceland. Originally from Sweden.
Guthrum, colonised England (Danelaw).
Ingvar the Far-Travelled, the leader of the last great Swedish Viking expedition, which pillaged the shores of the Caspian Sea
Ivar the Boneless, disabled son of Ragnar Lodbrok who, despite having to be carried on a shield, conquered York
Ingólfur Arnarson, colonised Iceland
Oleg of Kiev, conquered Kiev, founded Kievan Rus' and attacked Constantinople
Ragnar Lodbrok, captured Paris
Rollo of Normandy, founder of Normandy
Rurik, founder of the Rus' rule in Eastern Europe



 Later life, death, and legacy
Later life, death, and legacy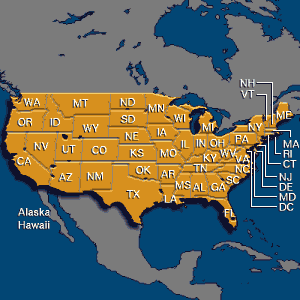
 Historical records
Historical records North America
North America